CPS 353: Internet Programming
Sessions and Security
Simon Miner
Gordon College
Last Modified: 11/13/2013
Selected content adapted from material by Marty Stepp, Jessica Miller, and Victoria Kirst © 2012. Used by permission.
Agenda
- Scripture (Colossians 2) and Prayer
- Check-in
- Sessions
- Web Security
- Homework 7
Check-in
- Syllabus Updates
- Homework 6
- Milestone 6
- Nested routes -- Kenneth Burgess and Peter Story (?)
- Updating price totals
14.1: Cookie Basics
- 14.1: Cookie Basics
- 14.2: Programming with Cookies
- 14.3: Sessions
Stateful client/server interaction
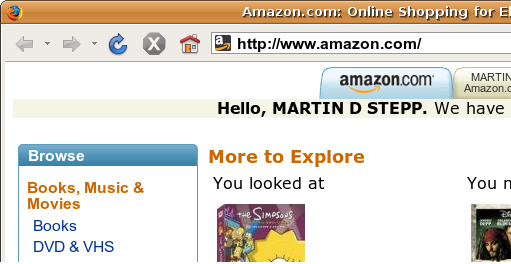
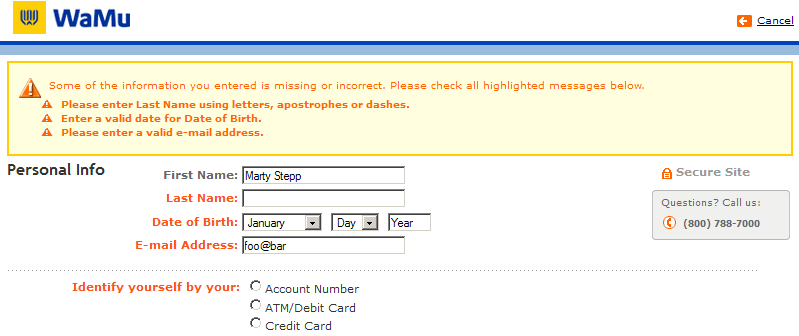
Sites like amazon.com seem to "know who I am." How do they do this? How does a client uniquely identify itself to a server, and how does the server provide specific content to each client?
- HTTP is a stateless protocol; it simply allows a browser to request a single document from a web server
- today we'll learn about pieces of data called cookies used to work around this problem, which are used as the basis of higher-level sessions between clients and servers
What is a cookie?

- cookie: a small amount of information sent by a server to a browser, and then sent back by the browser on future page requests
- cookies have many uses:
- authentication
- user tracking
- maintaining user preferences, shopping carts, etc.
- a cookie's data consists of a single name/value pair, sent in the header of the client's HTTP GET or POST request
How cookies are sent
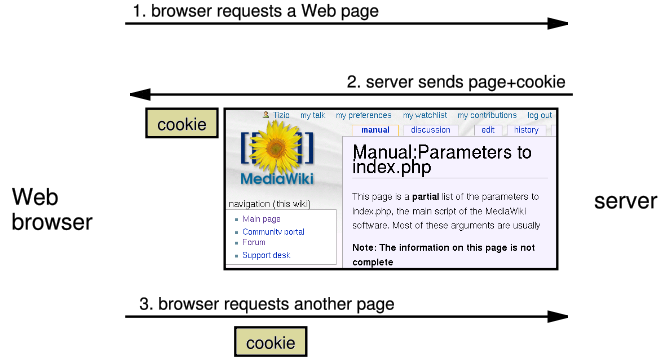
- when the browser requests a page, the server may send back a cookie(s) with it
- if your server has previously sent any cookies to the browser, the browser will send them back on subsequent requests
- alternate model: client-side JavaScript code can set/get cookies
Myths about cookies
- Myths:
- Cookies are like worms/viruses and can erase data from the user's hard disk.
- Cookies are a form of spyware and can steal your personal information.
- Cookies generate popups and spam.
- Cookies are only used for advertising.
- Facts:
- Cookies are only data, not program code.
- Cookies cannot erase or read information from the user's computer.
- Cookies are usually anonymous (do not contain personal information).
- Cookies CAN be used to track your viewing habits on a particular site.
A "tracking cookie"
- an advertising company can put a cookie on your machine when you visit one site, and see it when you visit another site that also uses that advertising company
- therefore they can tell that the same person (you) visited both sites
- can be thwarted by telling your browser not to accept "third-party cookies"
Where are the cookies on my computer?

- IE: HomeDirectory\Cookies
- e.g. C:\Documents and Settings\jsmith\Cookies
- each is stored as a
.txtfile similar to the site's domain name
- Chrome: C:\Users\username\AppData\Local\Google\Chrome\User Data\Default
- Firefox: HomeDirectory\.mozilla\firefox\???.default\cookies.txt
- view cookies in Firefox preferences: Privacy, Remove Individual Cookies...
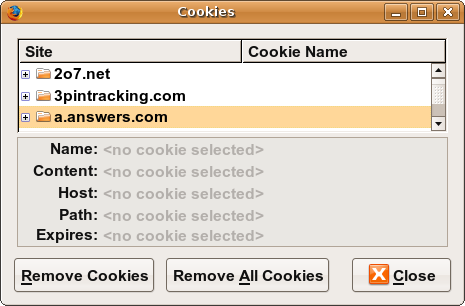
- view cookies in Firefox preferences: Privacy, Remove Individual Cookies...
How long does a cookie exist?
- session cookie : the default type; a temporary cookie that is stored only in the browser's memory
- when the browser is closed, temporary cookies will be erased
- can not be used for tracking long-term information
- safer, because no programs other than the browser can access them
- persistent cookie : one that is stored in a file on the browser's computer
- can track long-term information
- potentially less secure, because users (or programs they run) can open cookie files, see/change the cookie values, etc.
14.2: Programming with Cookies
- 14.1: Cookie Basics
- 14.2: Programming with Cookies
- 14.3: Sessions
Cookies in JavaScript
document.cookie = "username=smith"; // setting two cookies document.cookie = "password=12345"; document.cookie = "age=29; expires=Thu, 01-Jan-1970 00:00:01 GMT"; // deleting a cookie ...
// (later) var allCookies = document.cookie.split(";"); // ["username=smith", "password=12345"] for (var i = 0; i < allCookies.length; i++) { var eachCookie = allCookies[i].split("="); // ["username", "smith"] var cookieName = eachCookie[0]; // "username" var cookieValue = eachCookie[1]; // "smith" ... }
- JS has a global
document.cookiefield (a string) -
you can manually set/get cookie data from this field (sep. by
;), and it will be saved in the browser - to delete a cookie, set it to 'expire' in the past
Setting a cookie in PHP
setcookie("name", "value");
setcookie("username", "martay");
setcookie("favoritecolor", "blue");
setcookiecauses your script to send a cookie to the user's browsersetcookiemust be called before any output statements (HTML blocks,print, orecho)- you can set multiple cookies (20-50) per user, each up to 3-4K bytes
- technically, a cookie is just part of an HTTP header, and it could be set using PHP's
headerfunction (but this is less convenient, so you would not want to do this):
header("Set-Cookie: username=martay; path=/; secure");
Retrieving information from a cookie
$variable = $_COOKIE["name"]; # retrieve value of the cookie
if (isset($_COOKIE["username"])) {
$username = $_COOKIE["username"];
print("Welcome back, $username.\n");
} else {
print("Never heard of you.\n");
}
print("All cookies received:\n");
print_r($_COOKIE);
- any cookies sent by client are stored in
$_COOKIESassociative array - use
issetfunction to see whether a given cookie name exists
unsetfunction deletes a cookie
Setting a persistent cookie in PHP
setcookie("name", "value", timeout);
$expireTime = time() + 60*60*24*7; # 1 week from now
setcookie("CouponNumber", "389752", $expireTime);
setcookie("CouponValue", "100.00", $expireTime);
Removing a persistent cookie
setcookie("name", "", time() - 1);
setcookie("CouponNumber", "", time() - 1);
- if the server wants to remove a persistent cookie, it should set it again, passing a timeout that is prior to the present time
Cookies in Rails
# Set a simple session cookie.
cookies[:user_name] = "aardvark"
# Set a cookie that expires in 1 hour.
cookies[:login] = { :value => "XJ12", :expires => 1.hour.from_now }
# Get cookie informaion.
cookies[:user_name] # => "david"
cookies.size # => 2
# Delete cookies.
cookies.delete :user_name
14.3: Sessions
- 14.1: Cookie Basics
- 14.2: Programming with Cookies
- 14.3: Sessions
What is a session?
- session: an abstract concept to represent a series of HTTP requests and responses between a specific Web browser and server
- HTTP doesn't support the notion of a session, but PHP and Rails do
- sessions vs. cookies:
- a cookie is data stored on the client
- a session's data is stored on the server (only 1 session per client)
- sessions are often built on top of cookies:
- the only data the client stores is a cookie holding a unique session ID
- on each page request, the client sends its session ID cookie, and the server uses this to find and retrieve the client's session data
How sessions are established in PHP
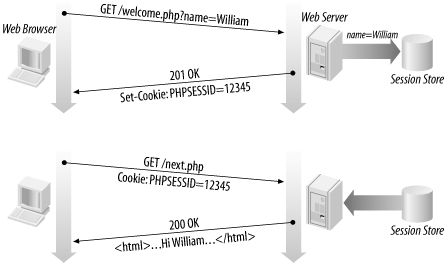
- client's browser makes an initial request to the server
- server notes client's IP address/browser, stores some local session data, and sends a session ID back to client
- client sends that same session ID back to server on future requests
- server uses session ID to retrieve the data for the client's session later, like a ticket given at a coat-check room
Sessions in PHP: session_start
session_start();
session_startsignifies your script wants a session with the user- must be called at the top of your script, before any HTML output is produced
- when you call
session_start:- if the server hasn't seen this user before, a new session is created
- otherwise, existing session data is loaded into
$_SESSIONassociative array - you can store data in
$_SESSIONand retrieve it on future pages
- complete list of PHP session functions
Accessing session data in PHP
$_SESSION["name"] = value; # store session data $variable = $_SESSION["name"]; # read session data if (isset($_SESSION["name"])) { # check for session data
if (isset($_SESSION["points"])) {
$points = $_SESSION["points"];
print("You've earned $points points.\n");
} else {
$_SESSION["points"] = 0; # default
}
- the
$_SESSIONassociative array reads/stores all session data - use
issetfunction to see whether a given value is in the session
Where is PHP session data stored?
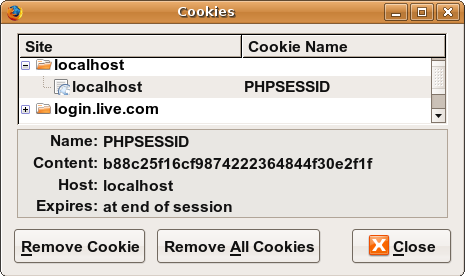
- on the client, the session ID is stored as a cookie with the name
PHPSESSID - on the server, session data are stored as temporary files such as
/tmp/sess_fcc17f071... - you can find out (or change) the folder where session data is saved using the
session_save_pathfunction - for very large applications, session data can be stored into a SQL database (or other destination) instead using the
session_set_save_handlerfunction
Session timeout
- because HTTP is stateless, it is hard for the server to know when a user has finished a session
- ideally, user explicitly logs out, but many users don't
- client deletes session cookies when browser closes
- server automatically cleans up old sessions after a period of time
- old session data consumes resources and may present a security risk
- adjustable in PHP server settings or with
session_cache_expirefunction - you can explicitly delete a session by calling
session_destroy
Browsers that don't support cookies
session_start(); # same as usual # Generate a URL to link to one of our site's pages # (you probably won't ever need to do this) $orderUrl = "/order.php?PHPSESSID=" . session_id();
- if a client's browser doesn't support cookies, it can still send a session ID as a query string parameter named
PHPSESSID- this is done automatically;
session_startdetects whether the browser supports cookies and chooses the right method
- this is done automatically;
- if necessary (such as to build a URL for a link on the page), the server can find out the client's session ID by calling the
session_idfunction
Ending a session
session_destroy();
session_destroyends your current session- potential problem: if you call
session_startagain later, it sometimes reuses the same session ID/data you used before - if you may want to start a completely new empty session later, it is best to flush out the old one:
session_destroy(); session_regenerate_id(TRUE); # flushes out session ID number session_start();
Rails Sessions
-
Rails makes a
sessionhash available to your views and controllers- Allows small amounts of data to persist across requests
- Identified by a unique session id in a cookie - cannot be transmitted in a URL
- Actual session data can be stored in a variety of ways -- cookies (default), database, server-side cache
- Session data used to look up other information
class ApplicationController < ActionController::Base
private
# Finds the User with the ID stored in the session with the key
# :current_user_id This is a common way to handle user login in
# a Rails application; logging in sets the session value and
# logging out removes it.
def current_user
@_current_user ||= session[:current_user_id] &&
User.find_by(id: session[:current_user_id])
end
end
Rails Sessions (Continued)
Storing data in a session...
class LoginsController < ApplicationController
# "Create" a login, aka "log the user in"
def create
if user = User.authenticate(params[:username], params[:password])
# Get brand new session data for this newly logged in user
reset_session
# Save the user ID in the session so it can be used in
# subsequent requests
session[:current_user_id] = user.id
redirect_to root_url
end
end
end
Deleting data from a session...
class LoginsController < ApplicationController
# "Delete" a login, aka "log the user out"
def destroy
# Remove the user id from the session
@_current_user = session[:current_user_id] = nil
redirect_to root_url
end
end
Session best practices
- Don't store sensative data in sessions (i.e. login credentials, credit card numbers, etc.)
- Don't store personally identifiable data in sessions (i.e. email, username, etc.)
- Use sessions to store IDs that can be used as lookup keys to retrieve data about objects on the server
- Avoids direct object mapping
- Invoke session management logic (login, authentication, logout) at a single "choke point" in the application
- Application controller
- Controller callback functions (i.e.
before_action)
Implementing user logins
- many sites have the ability to create accounts and log in users
- most apps have a database of user accounts
- when you try to log in, your name/pw are compared to those in the database
See chapter 14 of the Agile Web Development with Rails 4 text for a good example of developing a simple login function
"Remember Me" feature
- How might an app implement a "Remember Me" feature, where the user's login info is remembered and reused when the user comes back later?
- Is this stored as session data? Why or why not?
- What concerns come up when trying to remember data about the user who has logged in?
15.1: Security Principles
- 15.1: Security Principles
- 15.2: Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
- 15.3: Validating Input Data
- 15.4: SQL Injection
- 15.5: Session-Based Attacks
Our current view of security

- until now, we have assumed:
- valid user input
- non-malicious users
- nothing will ever go wrong
- this is unrealistic!
The real world

- in order to write secure code, we must assume:
- invalid input
- evil users
- incompetent users
- everything that can go wrong, will go wrong
- everybody is out to get you
- botnets, hackers, script kiddies, KGB, etc. are out there
- assume nothing; trust no one
Attackers' goals

Why would an attacker target my site?
- Read private data (user names, passwords, credit card numbers, grades, prices)
- Change data (change a student's grades, prices of products, passwords)
- Spoofing (pretending to be someone they are not)
- Damage or shut down the site, so that it cannot be successfully used by others
- Harm the reputation or credibility of the organization running the site
- Spread viruses and other malware
Tools that attackers use
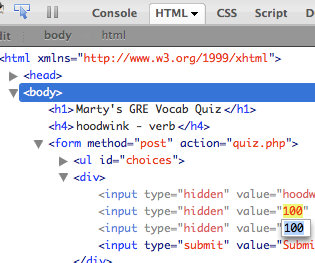
Assume that the attacker knows about web dev and has the same tools you have:
- Firebug
- extensions e.g. Web Dev Toolbar
- port scanners, e.g. nmap
- network sniffers, e.g. Wireshark, EtherDetect, Firesheep
Some kinds of attacks

- Denial of Service (DoS): Making a server unavailable by bombarding it with requests.
- Social Engineering: Tricking a user into willingly compromising the security of a site (e.g. phishing).
- Privilege Escalation: Causing code to run as a "privileged" context (e.g. "root").
- Information Leakage: Allowing an attacker to look at data, files, etc. that he/she should not be allowed to see.
- Man-in-the-Middle: Placing a malicious machine in the network and using it to intercept traffic.
- Session Hijacking: Stealing another user's session cookie to masquerade as that user.
- Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) or HTML Injection: Inserting malicious HTML or JavaScript content into a web page.
- SQL Injection: Inserting malicious SQL query code to reveal or modify sensitive data.
Information leakage
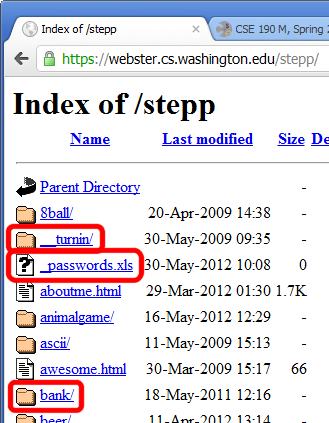
when the attacker can look at data, files, etc. that he/she should not be allowed to see
-
files on web server that should not be there
- or have too generous of permissions (read/write to all)
-
directories that list their contents (indexing)
- can be disabled on web server
-
guess the names of files, directories, resources
- see
loginfail.php, tryloginsuccess.php - see
user.php?id=123, tryuser.php?id=456 - see
/data/public, try/data/private
- see
15.2: Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
- 15.1: Security Principles
- 15.2: Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
- 15.3: Validating Input Data
- 15.4: SQL Injection
- 15.5: Session-Based Attacks
Cross-site scripting (XSS)
a flaw where a user is able to inject and execute arbitrary JavaScript code in your page
insecure.php?question=<script type='text/javascript'>alert('pwned');</script>
<h1>Your question is: <?php $_GET['question'] ?></h1>
- injected script code can:
- masquerade as the original page and trick the user into entering sensitive data
- steal the user's cookies
- masquerade as the user and submit data on their behalf (submit forms, click buttons, etc.)
- ...
- Reflected XSS rendered back to the user clicks on the link containing or activating it
- Stored XSS when bad code is persisted so that other users are vulnerabilt to it
- A sad but true real-world example of a XSS vulnerability
Securing against XSS
- one idea: disallow harmful characters
- XSS is impossible without < >
- can strip those characters from input, or reject the entire request if they are present
- another idea: allow them, but escape them
htmlspecialchars
|
returns an HTML-escaped version of a string |
$text = "<p>hi 2 u & me</p>";
$text = htmlspecialchars($text); # "<p>hi 2 u & me</p>"
html_safe, raw, etc. helper functions to render properly escaped HTML in a view15.3: Validating Input Data
- 15.1: Security Principles
- 15.2: Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
- 15.3: Validating Input Data
- 15.4: SQL Injection
- 15.5: Session-Based Attacks
What is form validation?
- validation: ensuring that form's values are correct
- some types of validation:
- preventing blank values (email address)
- ensuring the type of values
- integer, real number, currency, phone number, Social Security number, postal address, email address, date, credit card number, ...
- ensuring the format and range of values (ZIP code must be a 5-digit integer)
- ensuring that values fit together (user types email twice, and the two must match)
validates :voting_age, numericality: { greater_than_or_equal_to: 18 }
Client vs. server-side validation
Validation can be performed:
- client-side (in JavaScript, before the form is submitted)
- can lead to a better user experience, but not secure (why not?)
- server-side (in PHP code, after the form is submitted)
- needed for truly secure validation, but slower
- by the model (in Rails or within storage engine, after the form is submitted)
- often specific to the backend database being used
- all three
- best mix of convenience and security, but requires most effort to program
An example form to be validated
<form action="http://foo.com/foo.php" method="get"> <div> City: <input name="city" /> <br /> State: <input name="state" size="2" maxlength="2" /> <br /> ZIP: <input name="zip" size="5" maxlength="5" /> <br /> <input type="submit" /> </div> </form>
- Let's validate this form's data on the server...
Basic server-side validation code
$city = $_REQUEST["city"];
$state = $_REQUEST["state"];
$zip = $_REQUEST["zip"];
if (!$city || strlen($state) != 2 || strlen($zip) != 5) {
print "Error, invalid city/state/zip submitted.";
}
- basic idea: examine parameter values, and if they are bad, show an error message and abort. But:
- How do you test for integers vs. real numbers vs. strings?
- How do you test for a valid credit card number?
- How do you test that a person's name has a middle initial?
- (How do you test whether a given string matches a particular complex format?)
Regular expressions
/^[a-zA-Z_\-]+@(([a-zA-Z_\-])+\.)+[a-zA-Z]{2,4}$/
- regular expression ("regex"): a description of a pattern of text
- can test whether a string matches the expression's pattern
- can use a regex to search/replace characters in a string
- regular expressions are extremely powerful but tough to read
(the above regular expression matches email addresses) - regular expressions occur in many places:
- Java:
Scanner,String'ssplitmethod (CSE 143 sentence generator) - supported by PHP, JavaScript, and other languages
- many text editors (TextPad) allow regexes in search/replace
- Java:
Regular expressions in PHP (PDF)
- regex syntax: strings that begin and end with
/, such as"/[AEIOU]+/"
| function | description |
|---|---|
preg_match(regex, string)
|
returns TRUE if string matches regex
|
preg_replace(regex, replacement, string)
|
returns a new string with all substrings that match regex replaced by replacement |
preg_split(regex, string)
|
returns an array of strings from given string broken apart using given regex as delimiter (like explode but more powerful)
|
PHP form validation w/ regexes
$state = $_REQUEST["state"];
if (!preg_match("/^[A-Z]{2}$/", $state)) {
print "Error, invalid state submitted.";
}
preg_matchand regexes help you to validate parameters- sites often don't want to give a descriptive error message here (why?)
Basic regular expressions
/abc/
- in PHP, regexes are strings that begin and end with
/ - the simplest regexes simply match a particular substring
- the above regular expression matches any string containing
"abc":-
YES:
"abc","abcdef","defabc",".=.abc.=.", ... -
NO:
"fedcba","ab c","PHP", ...
-
YES:
Wildcards: .
- A dot
.matches any character except a\nline break/.oo.y/matches"Doocy","goofy","LooNy", ...
- A trailing
iat the end of a regex (after the closing/) signifies a case-insensitive match-
/mart/imatches"Marty Stepp","smart fellow","WALMART", ...
-
Special characters: |, (), \
|means OR/abc|def|g/matches"abc","def", or"g"- There's no AND symbol. Why not?
()are for grouping/(Homer|Marge) Simpson/matches"Homer Simpson"or"Marge Simpson"
\starts an escape sequence- many characters must be escaped to match them literally:
/ \ $ . [ ] ( ) ^ * + ? /<br \/>/matches lines containing<br />tags
- many characters must be escaped to match them literally:
Quantifiers: *, +, ?
*means 0 or more occurrences/abc*/matches"ab","abc","abcc","abccc", .../a(bc)*/matches"a","abc","abcbc","abcbcbc", .../a.*a/matches"aa","aba","a8qa","a!?xyz__9a", ...
+means 1 or more occurrences/a(bc)+/matches"abc","abcbc","abcbcbc", .../Goo+gle/matches"Google","Gooogle","Goooogle", ...
?means 0 or 1 occurrences/a(bc)?/matches"a"or"abc"
More quantifiers: {min,max}
{min,max}means between min and max occurrences (inclusive)/a(bc){2,4}/matches"abcbc","abcbcbc", or"abcbcbcbc"
- min or max may be omitted to specify any number
{2,}means 2 or more{,6}means up to 6{3}means exactly 3
Anchors: ^ and $
^represents the beginning of the string or line;
$represents the end-
/Jess/matches all strings that containJess;
/^Jess/matches all strings that start withJess;
/Jess$/matches all strings that end withJess;
/^Jess$/matches the exact string"Jess"only -
/^Mart.*Stepp$/matches"MartStepp","Marty Stepp","Martin D Stepp", ...
but NOT"Marty Stepp stinks"or"I H8 Martin Stepp"
-
-
(on the other slides, when we say,
/PATTERN/matches"text", we really mean that it matches any string that contains that text)
Character sets: []
-
[]group characters into a character set; will match any single character from the set/[bcd]art/matches strings containing"bart","cart", and"dart"- equivalent to
/(b|c|d)art/but shorter
- inside
[], many of the modifier keys act as normal characters/what[!*?]*/matches"what","what!","what?**!","what??!", ...
- What regular expression matches DNA (strings of A, C, G, or T)?
/[ACGT]+/
Character ranges: [start-end]
- inside a character set, specify a range of characters with
-/[a-z]/matches any lowercase letter/[a-zA-Z0-9]/matches any lower- or uppercase letter or digit
- an initial
^inside a character set negates it/[^abcd]/matches any character other than a, b, c, or d
- inside a character set,
-must be escaped to be matched/[+\-]?[0-9]+/matches an optional+or-, followed by at least one digit
- What regular expression matches letter grades such as A, B+, or D- ?
/[ABCDF][+\-]?/
Escape sequences
- special escape sequence character sets:
-
\dmatches any digit (same as[0-9]);\Dany non-digit ([^0-9]) -
\wmatches anyword character
(same as[a-zA-Z_0-9]);\Wany non-word char -
\smatches any whitespace character ( ,\t,\n, etc.);\Sany non-whitespace
-
- What regular expression matches dollar amounts of at least $100.00 ?
/\$\d{3,}\.\d{2}/
Regular expression PHP example
# replace vowels with stars $str = "the quick brown fox"; $str = preg_replace("/[aeiou]/", "*", $str); # "th* q**ck br*wn f*x" # break apart into words $words = preg_split("/[ ]+/", $str); # ("th*", "q**ck", "br*wn", "f*x") # capitalize words that had 2+ consecutive vowels for ($i = 0; $i < count($words); $i++) { if (preg_match("/\\*{2,}/", $words[$i])) { $words[$i] = strtoupper($words[$i]); } } # ("th*", "Q**CK", "br*wn", "f*x")
- notice how
\must be escaped to\\
Regular expressions in JavaScript
string.match(regex)- if string fits the pattern, returns the matching text; else returns
null - can be used as a Boolean truthy/falsey test:
var name = $("name").value;
if (name.match(/[a-z]+/)) { ... }
- if string fits the pattern, returns the matching text; else returns
- an
ican be placed after the regex for a case-insensitive matchname.match(/Aardvark/i)will match"aardvark","AaRdVaRk", ...
Replacing text with regular expressions
string.replace(regex, "text")- replaces the first occurrence of given pattern with the given text
var str = "Marty Stepp";
str.replace(/[a-z]/, "x")returns"Mxrty Stepp"- returns the modified string as its result; must be stored
str = str.replace(/[a-z]/, "x")
- a
gcan be placed after the regex for a global match (replace all occurrences)str.replace(/[a-z]/g, "x")returns"Mxxxx Sxxxx"
- replace with empty string to use a regex as a filter
str = str.replace(/[^A-Z]+/g, "")turnsstrinto"MS"
Regular expressions in Ruby and Rails
matchmethod# 'haystack' does not contain the pattern 'needle', so doesn't match. /needle/.match('haystack') #=> nil # 'haystack' does contain the pattern 'hay', so it matches /hay/.match('haystack') #=> #<MatchData "hay">
- Patter surrounded with
//or%r{} - In calls to
validatesvalidates :url, format: { with: %r{\A(https?:)?//(\w+\.)+[a-z]{2,}} } validates :email, format: { with: /\A([^@\s]+)@((?:\w+\.)+[a-z]{2,})\Z/i }
15.4: SQL Injection
- 15.1: Security Principles
- 15.2: Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
- 15.3: Validating Input Data
- 15.4: SQL Injection
- 15.5: Session-Based Attacks
SQL injection
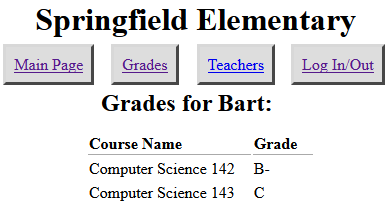
a flaw where the user is able to inject arbitrary SQL into your query
- This flaw often exists when a page accepts user input and inserts it bare into the query.
- example: simpsons grade lookup
- What kinds of SQL can we inject into the query? Why is this bad?
A SQL injection attack
-
The query in the Simpsons PHP code is:
$query = "SELECT * FROM students WHERE username = '$username' AND password = '$password'";
- Are there malicious values for the user name and password that we could enter?
- Password:
-
This causes the query to be executed as:
$query = "SELECT * FROM students WHERE username = '$username' AND password = '' OR '1'='1'";
- What will the above query return? Why is this bad?
Too true...
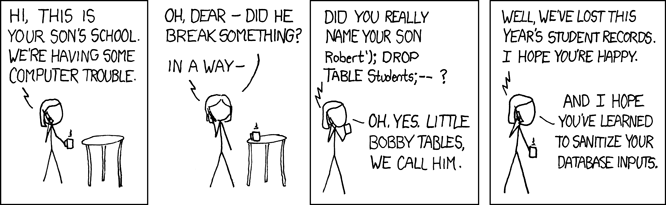
- injected SQL can:
- change the query to output others' data (revealing private information)
- insert a query to modify existing data (increase bank account balance)
- delete existing data (
; DROP TABLE students; --) - bloat the query to slow down the server (
JOIN a JOIN b JOIN c ...)
Securing against SQL injection
- similar to securing against XSS, escape the string before you include it in your query
quote
|
returns a SQL-escaped version of a string |
$username = $db->quote($_POST["username"]); $password = $db->quote($_POST["password"]); $query = "SELECT name, ssn, dob FROM users WHERE username = $username AND password = $password";
- replaces
'with\', etc., and surrounds with quotes
Parameterized Queries
- An even better approach...
new_users = Users.where( 'created_at > ?', 3.days.ago ); - Yields the following SQL query
selct * from users where created > ? - Passes the result of
3.days.agoas a parameter - ? in where clause referred to as placeholder or beind variable
- Has additional advantages
- Avoides annoying database-specific quoting issues
- In Oracle:
- 'Aardvark's' gets escaped to 'Aarkdvark''s'
- 'Moe > Larry' gets escaped to 'Moe '||'>'||' Larry'
- In Oracle:
- More efficient: databae may compile the query one time and then call it with different values for bind variables (like a function)
- Avoides annoying database-specific quoting issues
Injection attacks are not limited to SQL
- HTML injection
insecure.php?question=<h1>Run away. This site will virus your computer!</h1>
<h1>Your question is: <?php $_GET['question'] ?></h1>
- OS Injection
<?php include( $_GET["file"] ) ?>
15.5: Session-Based Attacks
- 15.1: Security Principles
- 15.2: Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
- 15.3: Validating Input Data
- 15.4: SQL Injection
- 15.5: Session-Based Attacks
Man-in-the-middle attack
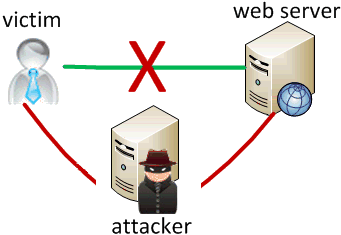
when the attacker listens on your network and reads and/or modifies your data
- works if attacker can access and compromise any server/router between you and your server
- also works if you are on the same local area or wifi network as the attacker
- often, the attacker still sends your info back and forth to/from the real server, but he silently logs or modifies some of it along the way to his own benefit
- e.g. listens for you to send your user name / password / credit card number / ...
Secure HTTP (HTTPS)

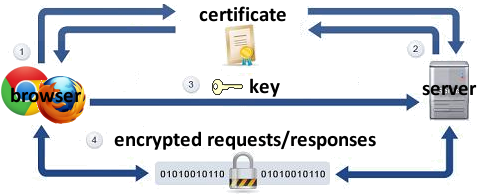
- HTTPS: encrypted version of HTTP protocol
-
all messages between client and server are encrypted so men in the middle cannot easily read them
- Client encrypts messages using the server's public key
- Server decrypts client's messages using its private key
- servers can have certificates that verify their identity
Session hijacking
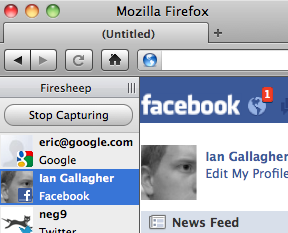
when the attacker gets a hold of your session ID and masquerades as you
-
exploit sites that use HTTPS for only the initial login:
- HTTPS: browser → server (POST login.php)
- HTTPS: browser ← server (login.php + PHPSESSID cookie)
- HTTP: browser → server (GET whatever.php + PHPSESSID cookie)
- HTTP: browser ← server (whatever.php + PHPSESSID cookie)
- attacker can listen to the network, get your session ID cookie, and make requests to the same server with that same session ID cookie to masquerade as you!
- example: Firesheep
Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF)

when the attacker tricks you into submitting a malicious request on their behalf
- Based on user's identity or authenticated state
- Performs undesired actions on the victim's behalf (i.e. make purchase, transfer money, etc.)
- Can occur when a user loads a page with an embedded CSRF attack - i.e. forum, blog post, email
- Example
- Assume a user is logged into his online bank account
- A CSRF attack could occur if the user loaded a page with a tag like this (containing a valid URL in the src attribute)
<img src="http://bank.com/transfer?acct=badguy&amount=100000" width="1" height="1" border="0">
Defending against CSRF attacks
- Limit the number and scope of single-request actions available to users
- Require additional authentication from users prior to allowing sensitive requests
- Anti-CSRF Token - require that a unique and expected token is included and verified with sensitive requests
- Rails does this automatically by including the following in your application controller
# Prevent CSRF attacks by raising an exception. # For APIs, you may want to use :null_session instead. protect_from_forgery with: :exception
- Creates a unique token (based on session id) for POST requests
- Token is validated by JavaScript that reads meta tags rendered in your application layout
<%= csrf_meta_tags %>
- Rails does this automatically by including the following in your application controller
OWASP Top 10
OWASP (Open Web Application Security Project) provides tools and information to make software more secure.
- Injection
- Broken Authentication and Session Management
- Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
- Insecure Direct Object References
- Security Misconfiguration
- Sensitive Data Exposure
- Missing Function Level Access Control
- Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF)
- Using Components with Known Vulnerabilities
- Unvalidated Redirects and Forwards
Secure Development Best Practices
- Keep security in mind from the start of and throughout the development process
- Break your own code because the bad guys will if you don't
- Defense in-depth
- Engineer multiple levels of security
- If an attacker gets by one level, they may be thwarted by a subsequent level
- Example
- Secure encrypted communication via SSL/HTTPS
- Role based user authentication
- Strict input validation (to defend against XSS, SQL ingjection, CSRF, etc.)
- Backend data validation (in case data within internal storage systems is compromised)
- Sensitive data stored with strong encryption (i.e AES with at least 256 bit key)
- Use two-factor authentication -- User needs multiple pieces of data to access a restricted resoruc
- Something you know (i.e. passcode)
- Something you have (i.e. cell phone with authentication token)
- Something you are (i.e. fingerprint, retina scan)
Secure software development from a Christian perspective
- Defending the weak
- Fighting against evil
- An ongoing mission
- Success in secure software development is measured by what does not happen